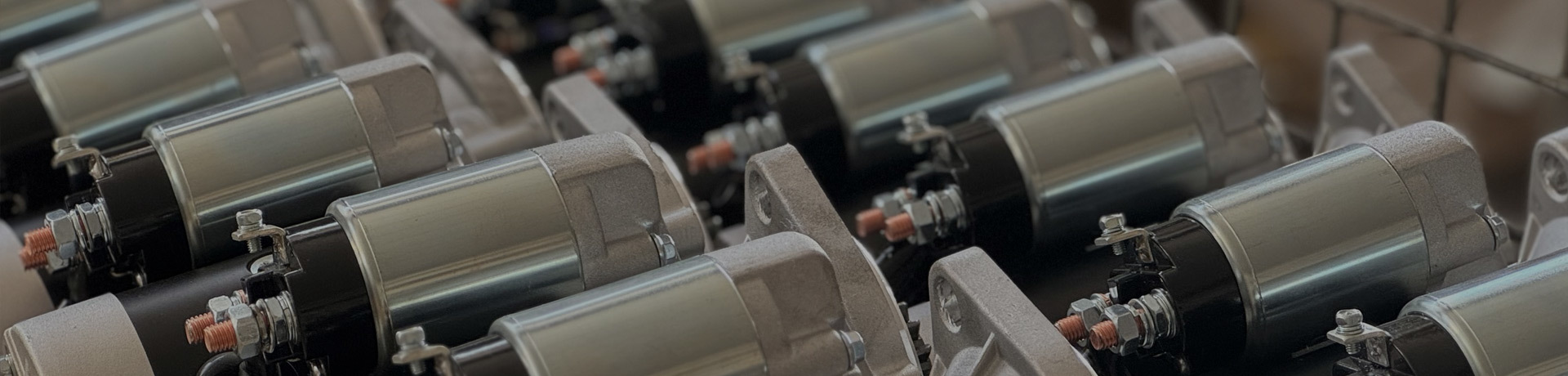
The operating principle varies across different engine types.
Release time:
2025-04-17
Intake: Air (or a mixture of air and fuel) is drawn into the cylinder. Compression: The piston's movement compresses the gas within the cylinder, increasing its temperature and pressure. Combustion (or work): In an internal combustion engine, fuel burns within the cylinder, producing high-temperature, high-pressure gas that pushes the piston; in an external combustion engine, the working medium expands due to an external heat source, pushing the piston. Exhaust: The exhaust gas is expelled from the cylinder.
Intake: Air (or a mixture of air and fuel) is drawn into the cylinder.
Compression: The piston's movement compresses the gas within the cylinder, increasing its temperature and pressure.
Combustion (or work): In an internal combustion engine, fuel burns within the cylinder, producing high-temperature, high-pressure gas that pushes the piston; in an external combustion engine, the working medium expands due to an external heat source, pushing the piston.
Exhaust: The exhaust gas is expelled from the cylinder.
Tag:
Related news
Message
* Please keep your phone open, we will get in touch with you in time